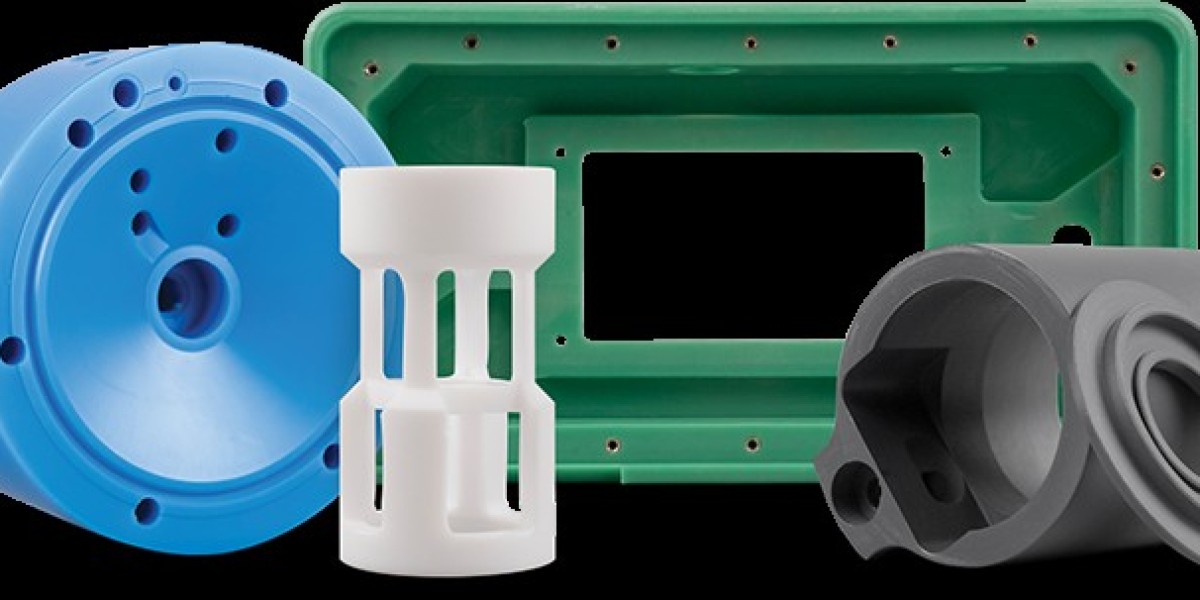
Machined plastic parts refer to components fabricated from various types of plastic materials through precise machining processes such as milling, turning, drilling, and cutting. These parts are custom-made to meet specific design and functional requirements, ensuring they fit perfectly within complex assemblies or machinery. Machining plastic involves working with materials like Nylon, PVC, PVDF, and others to create parts that are lightweight, durable, and resistant to wear and corrosion.
Definition of Machined Parts
Machined parts are components produced by removing material from a solid block (known as a workpiece) through controlled machining processes. These parts can be made from metals, plastics, or composites, and are typically used in applications where high precision, tight tolerances, and specific shapes are required. Machining allows for the creation of complex geometries and features that may not be achievable through other manufacturing methods.
Industrial Use Case of Machined Plastic Parts
Machined plastic parts are essential in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and industrial machinery. In the automotive industry, for instance, machined plastic parts are used in the production of gears, bearings, and bushings that require high precision and low friction. In the medical field, these parts are utilized in surgical instruments, prosthetics, and diagnostic equipment, where biocompatibility and sterilization are critical. The electronics industry relies on machined plastic parts for insulating components, connectors, and housings, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices.
How Machined Plastic Parts Improve Efficiency
The use of machined plastic parts offers several advantages that contribute to improved efficiency in manufacturing and operational processes. First, plastics are generally lighter than metals, reducing the overall weight of machinery and products. This weight reduction leads to lower energy consumption and improved performance, particularly in automotive and aerospace applications. Additionally, plastics can be machined more quickly and cost-effectively than metals, resulting in faster production times and lower manufacturing costs.
Moreover, the ability to machine plastics with high precision allows for the creation of parts with tight tolerances, ensuring a perfect fit in assemblies and reducing the need for rework or adjustments. This precision machining also enhances the performance and lifespan of the parts, leading to fewer failures and less maintenance over time. As a result, machined plastic parts contribute to greater efficiency, reliability, and cost savings across various industries.
Machined Plastic Parts Industrial Material Safety and Reliability
When it comes to industrial applications, the safety and reliability of machined plastic parts are of utmost importance. Plastics offer several inherent advantages in this regard, including resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. This makes them ideal for use in harsh environments where metal parts might degrade or fail. Furthermore, plastics are non-conductive, providing electrical insulation and reducing the risk of short circuits or electrical failures in electronic applications.
The reliability of machined plastic parts is further enhanced by the precision and consistency of the machining process. By ensuring that each part meets exact specifications, manufacturers can guarantee that the parts will perform as intended, even in demanding conditions. Additionally, many plastics used in machining, such as PVDF and PEEK, have excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and toughness, which contribute to the long-term durability and safety of the parts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, machined plastic parts play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering a combination of precision, efficiency, and reliability that is essential for various industrial applications. Their lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties make them an attractive alternative to metal parts, especially in industries where weight reduction and chemical resistance are critical. For high-quality machined plastic parts, Petron Thermoplast is a trusted provider, offering a wide range of materials and machining services to meet your specific needs.
FAQs
What types of plastics are commonly used for machined plastic parts? Common plastics used for machined parts include Nylon, PVC, PVDF, PEEK, and PTFE, each offering unique properties suited for different applications.
Can machined plastic parts withstand high temperatures? Yes, certain plastics like PEEK and PVDF have excellent thermal stability, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
How do machined plastic parts compare to metal parts in terms of strength? While plastics are generally not as strong as metals, advanced engineering plastics can offer comparable strength with the added benefits of corrosion resistance and lighter weight.
Are machined plastic parts more cost-effective than metal parts? Yes, machining plastics is often faster and less expensive than machining metals, leading to cost savings in both production and material costs.
What industries benefit most from using machined plastic parts? Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and industrial machinery benefit from the use of machined plastic parts due to their precision, durability, and material properties